Additive manufacturing has become an integral part of the companies regardless of their industry. From manufacturing automobile’s metal parts to prototypes, this tech is proving its mettle. With a market size of more than 25 billion dollars, industries are leveraging different available types of 3d printing.
On a broader perspective, there are a total of ten different types of additive manufacturing technologies available. In this post, we will explore all these other advancements and know more about their robust applications.
Fused deposition modeling (FDM)
This 3d printing technology is based on a method called material extrusion, and it uses a continuous filament of thermoplastic to prepare parts. Filaments like PLA, ABS or PET are loaded into the printer, and they are passed through a heated nozzle pushed by a motor.
The printer’s head moves in the pre-set specific coordinates and deposits the filament on the building platform where the structure solidifies. FDM is a classic example of layer by layer printing which offers good quality for manufacturing products. You will easily find FDM 3d printing services for preparing your custom prototype or an old part. There are many prototype manufacturing companies in the market, but make sure to choose a reliable and experienced company.
Common applications:
- Electrical housings
- Jigs and fixtures
- Form and fit testings
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS technology uses an advanced powder bed fusion method for printing the objects. The thermoplastic powder includes Nylon 6, Nylon 11, or Nylon 12, and they are heated below their melting point for printing. First, this technology deposits a fine-thin layer of powder ( approx 0.1 mm) over the building platform.
After this, a laser beam starts scanning the surface and it sinters the powder selectivity. It means, this process solidifies a cross-section of the item. After this scanning process, the printing platform goes down by one layer, and the cycle continues until the object is fully ready.
Applications of SLS 3d printing service
- Manufacturing of functional parts
- Industrial equipment printing
- Manufacturing is electronics hardware
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography is among the oldest and famous 3d printing services available for manufacturing objects. SLA is based on a method which is called Vat Polymerization in which a source cures photopolymer resin in a vat of light.
This printing methodology uses mirrors which are also known as galvanometers, and they are placed on X-axis and Y-axis. These mirrors help the laser pointer to move across the vat of resin material and print in a cross-section area of the object.
Applications of this method:
- Proof of concept prototypes
- Wind-tunnel testing models
- Jigs & fixtures
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP works on the same 3d printing technologies as the SLA, but it has a digital light projector which is quite helpful in printing larger objects. In digital light processing, the projector flashes a single image for every layer all in a single go, and it makes the process faster.
In DLP, the light is focused over the resin by an ultraviolet light source like a lamp. The array of micromirrors guides the light projection on the building platform.
Applications of DLP:
- Investment casting patterns
- Functional testing prototypes
- Visual prototypes for product’s photoshoot
PLA 3d printing

PLA 3d printing services are the most commonly used additive manufacturing method that is efficient and cost-effective. For beginners who are thinking of printing their first 3d model, this technology is the best as the PLA filaments are biodegradable.
If you are thinking about getting started with additive manufacturing, you can buy 3d printer in India and opt for this PLA printing technology. This additive method is suited best for printing non-functional prototyping, and decorative for educational purposes.
Applications of PLA
- For printing automotive tools
- Jigs and fixtures
- Non-functional prototypes and representative models
Sand Binder Jetting
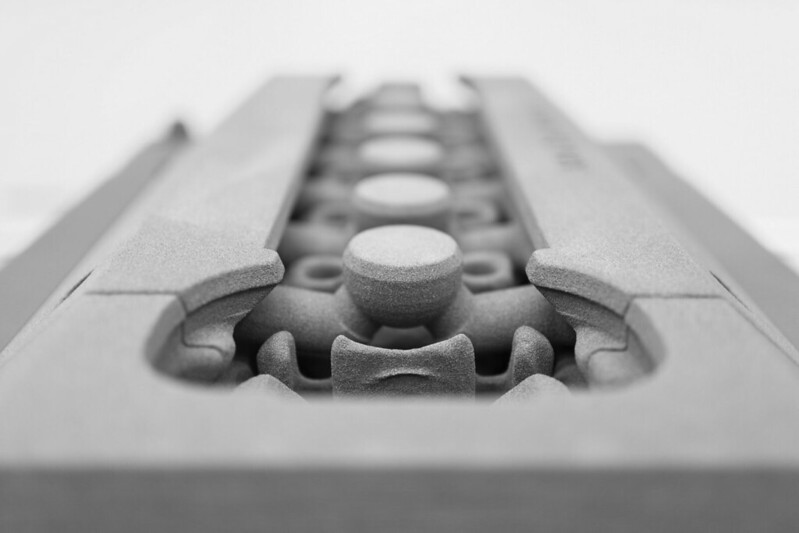

This additive manufacturing process uses a binder jetting process for printing the object. It’s quite similar to SLS as this process also needs an initial powder layer. In sand binder jetting, silica or sand are used on the building platform.
In these manufacturing processes, instead of utilizing the laser to sinter powder, the head deposits the droplets of the binder for producing the layers of the object. After the first layer is ready, the building platform is lowered, and a new powder layer is spread. For colourful models, the acrylic powder is used with the liquid binding. 3d printing service provider hubs use this method for:
- Sand moulds and casts patterns
- Full-colour prototypes
- Suitable for high volume production
Metal Binder Jetting
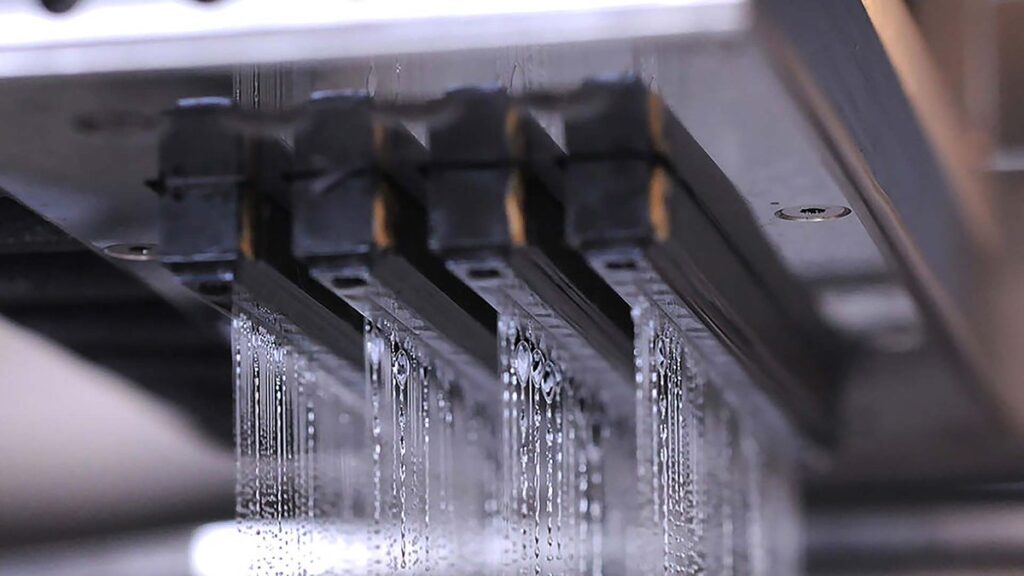

This additive manufacturing process is used for the fabrication of metal-based items. In this method, a polymer binding agent is used to bound the metal powder. This metal printing technology can manufacture complex geometry with higher accuracy as compared to others.
Many additive manufacturing hubs offer professional metal 3d printing in Pune and other cities for producing metal prototypes. As compared to the powder bed fusion, the objects printed with this technology have lower mechanical properties.
Metal Binder Jetting applications:
- Low-functional metal parts
- Full-colour 3d printed objects
- Suitable for large volumes prototypes
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
SLM is based on a metal powder bed fusion method in which the metal particles are fused using a heat source. Stainless steel, titanium, aluminium are some of the materials used in this technology.
Selective Laser Melting utilizes a laser to form a homogeneous part by melting the metal powder. This method sometimes does need support while printing complex geometries. Using supports reduce the chances of structural distortion during the production of objects.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering is similar to SLM, and it uses metal alloys to print the objects. In DMLS, the laser fuses the metal powder on a molecular level for final product production.
SLM additive manufacturing applications:
- Complex industrial tooling
- Production of dental and engineering parts
- High pressure resistant functional objects
These are the commonly utilized additive manufacturing techniques for producing prototypes or high-performance parts. If you are interested in this future-focused technology, you can easily buy a 3d printer in India online and explore the untapped possibilities. You can also refer to online tutorials to learn the basics and start printing.