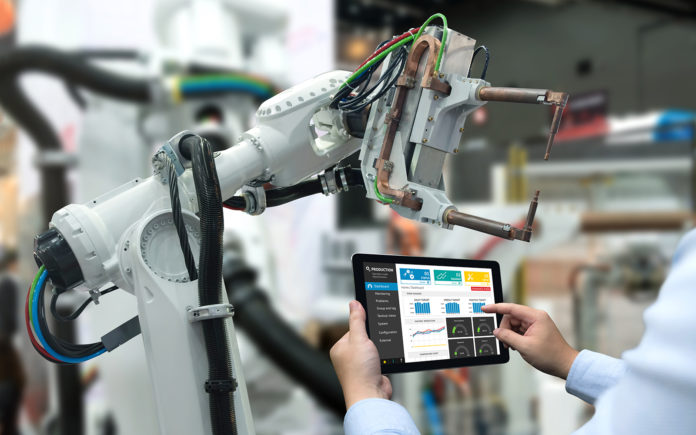
Extensive use of robotics makes automotive manufacturing one of the most automated supply chains in the world.
Did you know that robots have been an essential component in the production lines of the automotive industry for over 50 years? Today, robotics is present more than ever. Thanks to that, the efficiency and dependability of assembly lines increases.
The entire automotive industry relies on robots, but let’s takes a look at their crucial applications.
Intelligent Robotic Arms
Although robots can’t actually “see,” they have “eyes” that enable them to perform even the most precise tasks. You might have seen an industrial robotic arm equipped with a laser and camera. The robot receives immediate feedback from the camera, and that enables it to “see” what’s going on and know where it is.
Thanks to that, a robot can handle offsetting during component installation. Intelligent robotic arms have impressive accuracy when placing fenders, windshields, door panels, and other parts. They are a huge step forward compared to the “standard” robot arms used earlier.
Robotic Welders
Although you will need a large industrial robotic arm with adequate capabilities, some machines can even work on heavy body panels and perform spot welding. Depending on the robot size, it might be able to handle only brackets and mounts.
Robotic TIG and MIG welders maintain impressive accuracy with identical orientation during each cycle. That way, it ensures to comply with demanding welding standards. High-quality servomotors can also contribute to the performance and durability of robots in the automotive industry.
We even see robots that collaborate on massive production lines. If you want to keep the line going, robot handlers and welders need to work together. Before welders handle the necessary welding, handlers should place panels in the right position.
Robotic Assembly
Robotic arms have been assembling certain components in automotive manufacturing for a long time now. These arms can handle assembling parts and motors much faster than humans. They are also capable of wheel mounting, screw driving, windshield installation, and other tasks.
Robot Painters
It is hard to find experienced automotive painters who know how to do their job. Additionally, the job involves inhaling various toxic compounds, which is another reason why there is a shortage of workers. That is where robotic arms come into play.
These machines can maintain optimal paint consistency as long as they are programmed properly. Thanks to that, they will be efficient and cover huge areas quickly while minimizing waste. You can also use robotic arms for primers, sealants, and adhesives.
Transferring Components
Certain actions are very risky for human workers, such as adding molten metal to a foundry or loading CNC machines. That is why it is logical that robots replace them. However, these tasks can only be performed by big industrial robots. Small robotic arms can still be useful for other tasks of loading and unloading.
Material Removal
The biggest advantage of robotic arms is that they can handle multiple tasks within the same path. That can come in handy for trimming and cutting. However, if you want optimal accuracy, make sure to choose robots that come with the technology of force sensing. These can cut fabric, polish molds, and trim flash from plastic molding.
Internal Logistics
Do you need to move raw materials or components from a particular area in the warehouse to the factory floor? Autonomous mobile robots can help to replace manual material transfer, which can subsequently increase productivity.
The great part about using robotics in automotive manufacturing is that it has never been so accessible. Thanks to that, we can see production lines becoming more efficient every day.
Robotics doesn’t put the human workers in danger of staying without a job because they are required for quality control and final touches. However, there is no doubt that robotics can help to speed up the process and reduce overall manufacturing costs.